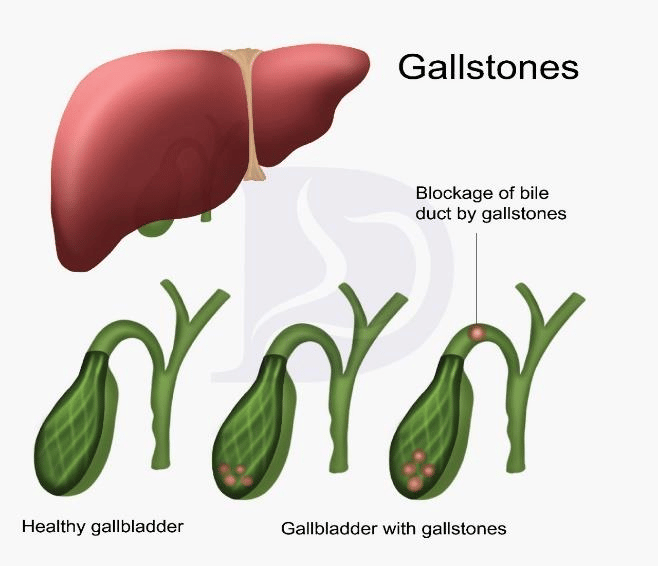
Gallstones/cholelithiasis
Bile Stones:
Normally our bile contains enough chemicals to dissolve the cholesterol excreted by our liver. But if our liver excretes more cholesterol than our bile can dissolve, the excess cholesterol may form into crystals and turn into stones. ie, our bile contains too much of bilirubin.
Gall Bladder is a small pearl-shaped organ on the right side of our abdomen. Just beneath to the liver, the gall bladder releases a digestive fluid called bile that release in our small intestine.
Gall stones range in size from a small grain of sand to large as a small ball, some people has just one gall stone, while other develops many gall stones at the same time.